How to Measure Cell Tower Radiation
To measure cell tower radiation, utilize tools like spectrum analyzers and RF meters for real-time radiofrequency exposure levels, ensuring compliance with safety standards from bodies like the FCC. Consider environmental factors, such as terrain and obstructions, that may affect measurements.
Consistent monitoring and precise equipment calibration are essential for accurate data collection. For further insights into measurement methods and protocols, explore additional resources.
Disclaimer: As an affiliate, I may collect a share of sales from the links on this page.
Understanding Cell Tower Radiation

When you think about cell tower radiation, it’s essential to recognize that radiofrequency (RF) radiation is a significant component of our wireless communication infrastructure. This form of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation is emitted continuously by cell towers, cell phones, and other wireless devices. Studies conducted in proximity to antennas have shown a notable increase in the health effects on residents living near these installations. While transparency is vital, the health effects remain a subject of debate. Studies indicate potential risks such as radiofrequency sickness, cancer links, and neurological issues. Furthermore, continuous exposure day and night raises public health concerns. Living near a cell phone tower can increase the risk of health complications as children are particularly vulnerable due to their developing systems and deeper radiation absorption. Regulatory safety limits are often questioned, emphasizing the need for ongoing research.
Measurement Methods Overview
To effectively assess cell tower radiation, several measurement methods are utilized, each with distinct approaches and tools.
Field measurements involve recording RF power density in real time using spectrum analyzers or broadband meters at various locations, indoors and outdoors. Cell Tower Exposure Testing ensures accurate assessments of potential health risks from RF emissions.
Predictive methods estimate radiation levels by calculating power density based on antenna parameters.
Software simulations model RF exposure scenarios, accounting for terrain and environmental factors.
Site selection focuses on diverse environments and statistical reliability, ensuring thorough data collection.
Standards direct compliance assessments by comparing results against safety limits, ensuring that both direct measurements and simulations inform exposure evaluations accurately.
Equipment Used for Measurement
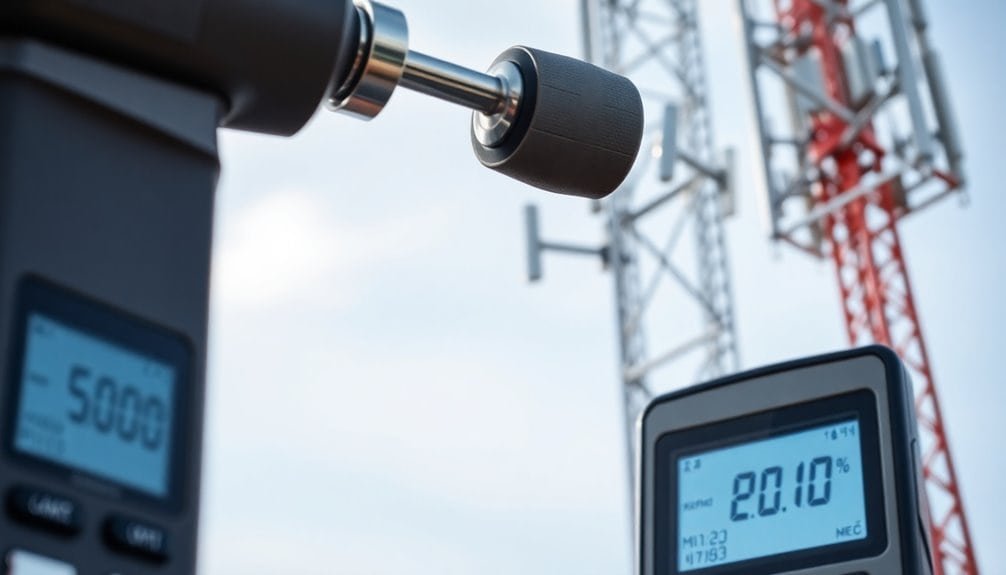

Evaluating cell tower radiation requires a variety of specialized equipment designed to provide accurate readings of radio frequency (RF) exposure.
RF meters measure RF exposure, ensuring safety standard compliance. Regular analysis affirms compliance with safety standards for public safety.
Broadband probes capture signals from all directions and encompass a wide frequency range.
Spectrum analyzers offer detailed insights on signal strength and frequency for thorough assessments.
Non-ionizing meters are the go-to choice for measuring cell tower radiation.
Handheld devices deliver portability for easy on-site evaluations.
When selecting equipment, consider frequency range, sensitivity, and calibration needs to maintain accuracy, ensuring that your measurements are reliable and compliant with safety standards.
Challenges in Measuring Radiation
Measuring cell tower radiation presents several technical challenges that can complicate accurate assessments. Variable power density fluctuates due to diverse usage patterns and multiple active channels. Instruments like isotropic broadband meters often struggle in multi-signal environments, resulting in measurement errors.
Additionally, RF energy arrives from various directions, requiring sensors that respond uniformly. To accurately evaluate variable power levels, timed signal averaging is essential.
Complex measurement environments at cell tower sites differ markedly from broadcast antenna locations. Factors such as distance, obstructions, and weather conditions further complicate assessments, demanding careful adjustments and a thorough understanding of surrounding elements influencing RF propagation.
Standards and Guidelines for Exposure

Establishing effective standards and guidelines for exposure to cell tower radiation is essential for public safety. The FCC sets the maximum permissible exposure level at approximately 580 microwatts per square centimeter. Other countries enforce stricter limits.
Exposure guidelines are often based on the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), measuring how RF energy absorbs into the body. Occupational limits allow up to 5000 microwatts per square centimeter, emphasizing the need for training and safety protocols.
The WHO classifies RF radiation as possibly carcinogenic, prompting ongoing debate about long-term health effects. Knowledge of these standards helps you assess your exposure effectively.
Applications of Measured Data
The data collected from cell tower radiation measurements plays a significant role in various applications that impact public safety and technological advancement. Measured data guarantees compliance with safety guidelines set by regulatory bodies. It aids in health risk assessments, supporting studies on long-term radiation effects.
Researchers use this information for environmental impact studies, analyzing effects on wildlife. Additionally, it drives technological development, promoting innovations that reduce emissions while enhancing connectivity.
Public awareness improves through education about safety and potential risks. Ultimately, these applications foster informed decision-making, guaranteeing safe cell tower deployment and operation while addressing community concerns effectively.
Conducting On-Site Measurements
Conducting on-site measurements of cell tower radiation requires careful planning and execution to ascertain accurate results.
Start by selecting measurement sites near visible towers, guaranteeing a direct line of sight. Consider antenna orientation; radiation is strongest in the direction of maximum gain.
Use EMF detectors and RF meters for precise readings. Assess environmental factors, like buildings or trees, which can affect radiation levels.
Wear appropriate safety gear and safeguard access to data on the tower’s specs. Implement field measurements and repeat tests to capture variations.
This structured approach ascertains your assessments of RF exposure are both accurate and reliable.
Data Collection and Analysis
In order to effectively measure cell tower radiation, using meticulous data collection techniques is vital.
Employ frequency selective spectrum analysis to measure GSM power densities, following relevant guidelines. Utilize equipment like the Advantest R3131 spectrum analyzer for accurate power density measurements.
Analyze data statistically to confirm reliability and take measurements under real-life conditions. Calibrate your devices regularly to maintain accuracy.
Consider challenges such as signal variability, interference, and equipment limitations. Integrating multiple data points, including tower locations and timestamps, enhances your analysis.
This systematic approach enables a thorough understanding of radiation levels impacting public exposure effectively.
Reporting and Recommendations
To guarantee compliance and safety regarding cell tower radiation, adhering to established reporting requirements is crucial. The FCC guidelines outline the maximum public exposure limit of approximately 580 microwatts per square centimeter.
Operators must monitor exposure and guarantee adherence to these limits, reporting any non-compliance to regulatory bodies. Workers near cell towers should receive radiofrequency radiation training and maintain safe distances from antennas during operations.
Signage and barriers are necessary to restrict unauthorized access. Compliance with OSHA mandates is also essential for safety.
Regular engagement with communities ensures transparency and addresses concerns regarding RF radiation effectively. Additionally, understanding the potential health risks of electromagnetic radiation can help inform communities about safety measures and exposure limits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Health Risks Are Associated With Cell Tower Radiation Exposure?
Cell tower radiation exposure might pose several health risks. You could face concerns like increased cancer risk, genetic damage, neurological issues, sleep disturbances, and even symptoms of Radiofrequency sickness, emphasizing the need for further research and regulation.
How Often Should Cell Tower Radiation Be Measured?
When it comes to measuring cell tower radiation, you should guarantee regular checks to keep things on the up and up. Typically, periodic measurements are enough to guarantee safety and compliance with established standards.
Can I Measure Cell Tower Radiation at Home?
Yes, you can measure cell tower radiation at home. Using an RF meter, you’ll assess electromagnetic fields in your environment. Be sure to compare your readings with safety guidelines to guarantee compliance and reduce potential risks.
What Are the Most Common Frequencies for Cell Towers?
Imagine waves dancing in the air; the most common frequencies for cell towers include low-bands like 600 MHz and 700 MHz, while mid-bands like 850 MHz and 1900 MHz balance speed and coverage.
How Can I Request a Radiation Assessment for My Area?
To request a radiation assessment, research local service providers, gather information about nearby cell towers, and contact a company like EMF Services. They’ll schedule onsite measurements to evaluate RF radiation levels in your area.
Conclusion
Measuring cell tower radiation is crucial for understanding exposure levels. With the right tools and techniques, accurate assessments can be conducted.
Radiation isn’t inherently harmful, but knowing the metrics helps make informed decisions. Staying updated with technological advances ensures safety.
Monitoring radiation levels provides peace of mind and is more than just compliance. Are you ready to measure the invisible?